胰腺肿瘤易侵犯神经及血管,通常较早发生转移,临床可行根治性手术切除者不足20%,患者术后5年生存率低于6%[1]。放射性125I粒子以其独特的剂量学优势为胰腺癌患者提供了一种有效的治疗方法[2-4]。有文献报道,利用3D打印共面模板辅助放射性粒子植入治疗胰腺癌是一种安全、有效的引导工具,有助于125I粒子精准植入[5-6]。北京大学第三医院肿瘤放疗科在3D打印非共面模板辅助放射性粒子植入治疗头颈部、胸部、腹部、盆腔等部位肿瘤做了大量工作[7-9],应用3D打印模板辅助,术后验证的主要剂量指标均较好地[HJ2mm]达到了术前预计划要求,精确性良好。本研究比较放射性粒子植入治疗胰腺癌采用非共面模板和共面模板术前计划参数的差异,对比分析两种技术的优略,指导临床应用。
资料与方法1.一般临床资料:选取2017年1月至2019年5月于北京大学第三医院接受外照射的胰腺癌患者,共20例患者,男性14例,女性6例,中位年龄68岁(45~85岁),中位KPS 80(70~90),TNM分期Ⅲ期14例,Ⅳ期6例。入组标准:有病理学或细胞学检查确诊胰腺癌;KPS评分≥70;外科证实无法手术切除或患者拒绝行手术治疗;具有可测量和可评价的病灶;预计生存期≥3个月;无放疗禁忌证;没有广泛坏死和瘘;血常规、肝功能、肾功能等正常。排除标准:有胰腺癌局部放疗史;已经发生远处转移者;年龄≥85岁,全身状况(KPS)评分≤60;合并有心脏、肝脏等重要脏器功能不全者。本研究对收集剂量学数据进行分析,通过本院伦理委员会论证。
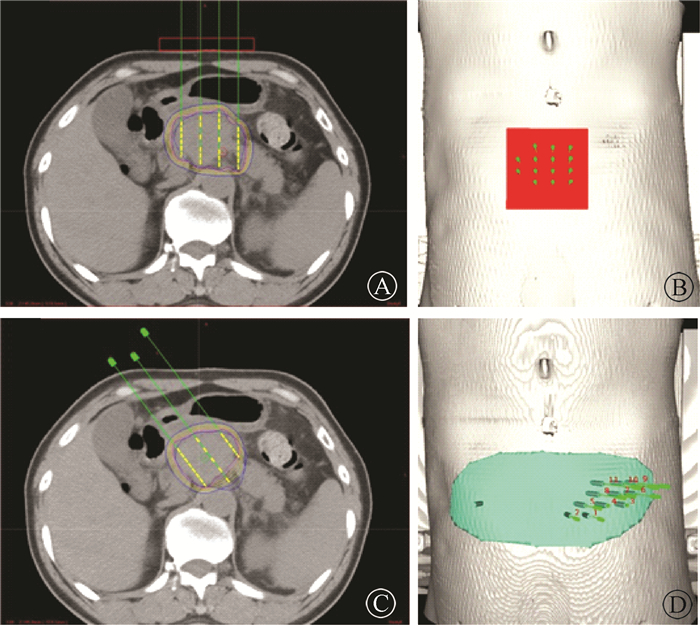
2.术前计划设计:患者术前1周内行螺旋定位CT扫描(荷兰Philips公司,Brilliance Bigbore CT),患者取仰卧位,真空垫固定体位,扫描层厚5 mm,于患者体表标记定位线及模板对位参考线。将CT定位图像传输至外照射计划系统(美国瓦里安公司,Eclipse 10.0),由放疗科医生勾画肿瘤靶区(gross tumor volume,GTV)即CT或MRI影像所显示的胰腺癌肿瘤区域以及腹腔、腹膜后阳性淋巴结,并勾画靶区周围危及器官,包括小肠、结肠、十二指肠、胃、脊髓。从外照射计划系统导入到近距离治疗计划系统(BTPS,北京天航科霖科技发展有限公司,KLSIRPS-3D),在同一图像序列中分别设计非共面模板计划与共面模板计划,计划内容包括设定处方剂量、确定插植针道方向及深度、优化粒子空间位置分布、计算GTV与周围危及器官剂量。优化时将处方剂量统一设定为110 Gy,粒子活度统一设定为0.4 mCi(1 Ci=3.7×1010 Bq),使GTV的D90(90% GTV接受的剂量)达到处方剂量。非共面计划设计时,个体化选择可规避肠道的进针角度;共面计划受模板角度影响,所有进针角度相同,见图 1。
|
图 1 计划设计典型层面及三维效果图 A.共面模板横断面图; B.共面模板3D效果图; C.非共面模版横断面图; D.非共面模板效果图 Figure 1 Planned and designed typical levels and 3D diagrams A.A cross section of a coplanar template; B.A 3D diagram of a coplanar template; C.A cross section of a non-coplanar template; D.A 3D diagram of a non- coplanar template |
3.计划对比与剂量评估:评价GTV的90%靶区体积的剂量(D90)、100%靶区体积的剂量(D100)、100%、150%和200%处方剂量的靶区体积(V100、V150和V200)、靶区外体积指数(EI)、适形指数(CI)和均匀性指数(HI)[8-9]。评价危及器官小肠、结肠、十二指肠、胃、脊髓的D2 cm3、D5 cm3(2 cm3和5 cm3器官所受到的照射剂量)。
4.统计学处理:采用SPSS 21.O软件进行数据分析。两种模板术前计划比较,符合正态分布的数据用x±s形式表示,采用配对t检验;不符合正态分布的数据,用中位数(Q25,Q75)形式表示,采用相关样本非参数检验(Wilcoxon法)。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果患者GTV平均体积为(79.66 ±53.2) cm3,共面计划比非共面计划的植入针数稍多18.63 vs. 16.45针(t=-3.239,P<0.05);粒子数相当(90.2颗vs. 91.01颗,P>0.05);靶区的D90、D100、V100、V150、V200、CI、EI、HI相差不显著(P>0.05);周围正常器官小肠、十二指肠、胃、脊髓的D2 cm3、D5 cm3相差不明显(P>0.05)。20例患者共面计划与非共面计划的各剂量学参数结果列于表 1。
|
|
表 1 共面计划和非共面计划的靶区及正常器官剂量学比较 Table 1 Dosimetric comparison of target areas and normal organs between coplanar and non-coplanar plans |
讨论
胰腺癌起病隐匿,恶性度高,早期诊断困难,发现时往往已经侵犯胰腺周围重要血管或已属中晚期,错过了最佳手术治疗时机。CT引导放射性125I粒子植入治疗不可切除胰腺癌疗效肯定,不仅可有效控制胰腺癌局部进展,而且可以有效减缓肿瘤生长速度,甚至缩小肿瘤体积,有效缓解疼痛,提高患者生活质量,且不良反应小、操作相对简单。但是粒子植入治疗中晚期胰腺癌剂量学方面还存在很多问题,模板的使用可使术后剂量分布达到术前计划设计要求[7-9],对于规范操作流程,进行前瞻性研究有非常重大的意义。
放射性粒子植人治疗的疗效直接取决于剂量分布,而剂量分布在很大程度上取决于插植针的空间分布(间距、深度、角度、平行程度等)[10]。平面穿刺模板可提高穿刺针位置的精确度,且统一化制作,成本低,但其在植入方向上无法灵活调整,多用于病灶形态较规则、穿刺方向单一、进针路径无危及器官阻挡的病变。3D打印非共面模板含有预设的插植针道信息和患者治疗区体表特征信息,具备了定位、定向功能,但是需要个体化制作模板,打印周期长,成本高, 因此合理选择模板类型,对开展后续研究、指导临床实践有重要价值。
放射性125I粒子植入治疗胰腺癌,3D打印非共面及共面模板都有使用,其植入方式主要受前部肠道影响,本研究针对非共面及共面计划的对比,非共面计划比共面计划使用的植入针减少了10%, 原因主要是前者针道间的间隔灵活性更好,可以任意间隔,而后者更局限,间隔是0.5 cm倍数,所以非共面计划的针道使用少。针道的减少,意味着创伤更小,手术时间更短。
总之,两种计划均可达到处方剂量,同时正常器官的剂量相差较小,各有特点,故需要根据具体情况进行选择。
利益冲突 所有研究者未因进行该研究而接受任何不正当的职务或财务利益,在此对研究的独立性和科学性予以保留
作者贡献声明 孙海涛负责整理临床材料,粒子植入计划设计,并采集数据结果,起草论文;王俊杰、姜玉良负责审核患者粒子植入计划并指导论文写作;吉喆、郭福新、陈意负责协助完善数据及数据分析
| [1] |
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, et al. Cancer statistics, 2014[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2014, 64(1): 9-29. DOI:10.3322/caac.21208 |
| [2] |
赵金, 邹晓明, 云哲琳, 等. 125I粒子术中植入治疗晚期胰腺癌的临床疗效[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2018, 24(12): 833-837. Zhao J, Zou XM, Yun ZL, et al. Clinical efficacy of implantation of 125I particles in the treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Chin J Hepato Surg, 2018, 24(12): 833-837. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2018.12.010 |
| [3] |
朱永强, 陈俊英, 郭剑峰. CT引导下125I粒子植入治疗晚期胰腺癌的临床疗效分析[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2011, 20(4): 283-286. Zhu YQ, Chen JY, Guo JF. CT-guided 125I seed implantation for the treatment of advanced pancreatic carcinoma:a clinical efficacy analysis[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2011, 20(4): 283-286. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2011.04.008 |
| [4] |
王俊杰, 修典荣, 冉维强, 等. 术中超声引导放射性125I粒子组织间植入治疗胰腺癌[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2007, 16(1): 34-37. Wang JJ, Xiu DR, Ran WQ, et al. Intraoperative ultrasound quided 125I seed implantation for unresectable pancreatic carcinoma[J]. Chin J Radiat Oncol, 2007, 16(1): 34-37. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:1004-4221.2007.01.008 |
| [5] |
陆健, 黄蔚, 贡桔, 等. 模板辅助CT引导放射性粒子植入治疗胰腺癌的临床应用价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2017, 51(12): 966-970. Lu J, Huang W, Gong J, et al. Clinical application value of template-assisted CT-guided radioactive seed implantation for pancreatic carcinoma[J]. Chin J Radiol, 2017, 51(12): 966-970. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2017.12.015 |
| [6] |
陆健, 郑云峰, 张欢, 等. CT导引下植入125I粒子治疗19例晚期胰腺癌的疗效观察[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2010, 19(7): 550-553. Lu J, Zheng YF, Zhang H, et al. CT-guided radioactive 125I-seed implantation for the treatment of pancreatic carcinoma:a clinical observation of 19 cases[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2010, 19(7): 550-553. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2010.07.011 |
| [7] |
姜玉良, 王皓, 吉喆, 等. CT引导辅助3D打印个体化非共面模板指导125I粒子治疗盆腔复发肿瘤剂量学研究[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2016, 25(9): 959-964. Jiang YL, Wang H, Ji Z, et al. Computed tomography image-guided and personalized 3D printed template-assisted 125I seed implantation for recurrent pelvic tumor:a dosimetric study[J]. Chin J Radiat Oncol, 2016, 25(9): 959-964. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2016.09.012 |
| [8] |
孙海涛, 姚丽红, 王俊杰, 等. 3D打印非共面模板引导125I粒子组织间近距离治疗盆腔肿瘤个体化设计[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2017, 37(7): 485-489. Sun HT, Yao LH, Wang JJ, et al. 3D-printing non-coplanar template assisted 125I seed implantation for pelvic tumor:individual template design method[J]. Chin J Radiol Med Prot, 2017, 37(7): 485-489. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5098.2017.07.002 |
| [9] |
吉喆, 姜玉良, 郭福新, 等. 3D打印个体化非共面模板辅助放射性粒子植入治疗恶性肿瘤的剂量学验证[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2016, 36(9): 662-666. Ji Z, Jiang YL, Guo FX, et al. Dosimetry verification of radioactive seed implantation for malignant tumor assisted by 3D printing individual guide template[J]. Chin J Radiol Med Prot, 2016, 36(9): 662-666. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5098.2016.09.005 |
| [10] |
Rembowska AME, Cook M, Hoskin PJ, et al. The stepping source dosimetry system as an extension of the manchester system[J]. Radiot Oncol, 1996, 39(39): 25. DOI:10.1016/0167-8140(96)87899-6 |
 2021, Vol. 41
2021, Vol. 41


